# 数组
最近在学习 Java 语言,顺便记录一下 Java 中常用的数组操作,大致的用法和 Python 不能说很像,只能说是一毛一样
# 一维数组
对于一维数组的常规操作,一般有数组元素遍历,求最大最小元素,筛选重复元素,元素从小到大排序,元素从大到小排序等等
# 数组元素遍历
- 元素按序遍历
import java.util.Arrays; | |
public class demo1 { | |
public static void main(String[] args) { | |
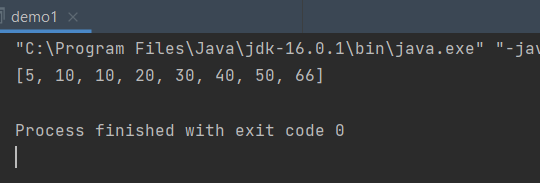
int[] arr={10,20,66,30,5,40,50,10}; | |
printArrays1(arr); // 遍历数组元素方法 1 | |
printArrays2(arr); // 遍历数组元素方法 2 | |
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); //Arrays 方法遍历元素 | |
} | |
public static void printArrays1(int[] a){ // 遍历数组元素方法 1 | |
if (a.length == 0){ // 判断数组是否为空 | |
System.out.println("[]"); | |
}else{ | |
System.out.print("["); | |
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { | |
if (i == a.length -1){ | |
System.out.println(a[i]+"]"); | |
}else{System.out.print(a[i]+ ", ");} | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
public static void printArrays2(int[] a){ // 遍历数组元素方法 2 | |
int max = 0; | |
if(a.length == 0){ // 判断数组是否为空 | |
System.out.println("[]"); | |
}else{ | |
System.out.print("["); | |
for (int i:a) { // 类似 Python foreach 语法糖 | |
if(a.length-1 != max){ | |
System.out.print(i+", "); | |
max++; | |
}else{System.out.println(i+"]");} | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
} |
- 运行结果
- 元素反序遍历
public class demo1 { | |
public static void main(String[] args) { | |
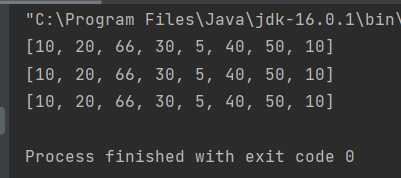
int[] arr={10,20,66,30,5,40,50,10}; | |
reverseArrays(arr); // 元素反序遍历 | |
} | |
public static void reverseArrays(int[] a){ // 元素反序遍历 | |
if (a.length == 0){ // 判断数组是否为空 | |
System.out.println("[]"); | |
}else{ | |
System.out.print("["); | |
for (int i = a.length-1; i >= 0; i--) { | |
if (i != 0){ | |
System.out.print(a[i]+ ", "); | |
}else{ | |
System.out.println(a[i]+"]"); | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
} |
- 运行结果
# 求最大最小数
public class demo1 { | |
public static void main(String[] args) { | |
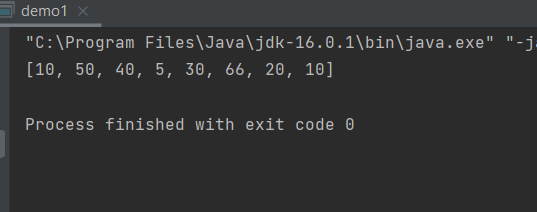
int[] arr={10,20,66,30,5,40,50,10}; | |
maxOfArrays(arr); // 求数组中最大元素 | |
minOfArrays(arr); // 求数组中最小元素 | |
} | |
public static void maxOfArrays(int[] a) { // 求数组中最大元素 | |
if (a.length == 0) { // 判断数组是否为空 | |
System.out.println("[]"); | |
} else { | |
int max=a[0]; | |
System.out.print("["); | |
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { | |
if (max < a[i]) { | |
max = a[i]; | |
} | |
} | |
System.out.println(max + "]"); | |
} | |
} | |
public static void minOfArrays(int[] a) { // 求数组中最小元素 | |
if (a.length == 0) { // 判断数组是否为空 | |
System.out.println("[]"); | |
} else { | |
int min = a[0]; | |
System.out.print("["); | |
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { | |
if (min > a[i]) { | |
min = a[i]; | |
} | |
} | |
System.out.println(min + "]"); | |
} | |
} | |
} |
- 运行结果
# 元素大小排序
- 冒泡排序
import java.util.Arrays; | |
public class demo1 { | |
public static void main(String[] args) { | |
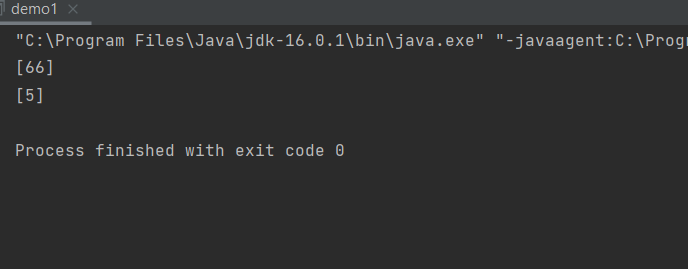
int[] arr = {10, 20, 66, 30, 5, 40, 50, 10}; | |
minToMax(arr); | |
} | |
public static void minToMax(int[] a){ | |
// 判断数组是否少于 2 个元素 | |
if(a.length < 2){ | |
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); | |
}else{ | |
int tmp = 0; | |
boolean flag; | |
for (int i = 0; i < a.length-1; i++) { | |
flag = false; | |
for (int j = a.length-1; j > i; j--) { | |
// 如果需要按从大到小排序,把 a [j]<a [j-1] 的符合更换成 > 即可 | |
if (a[j]<a[j-1]){ | |
tmp=a[j]; | |
a[j]=a[j-1]; | |
a[j-1]=tmp; | |
flag=true; | |
} | |
} | |
if(!flag){ | |
break; | |
} | |
} | |
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); | |
} | |
} | |
} |
- 运行结果